Training
RHCE Exam Objective: Use Firewalld
by jfargen on Nov.06, 2016, under Cert, RHCE, Training
Just going to cover the basics, for reference refer to manpage.
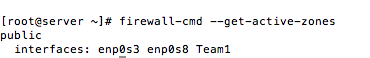
Check what the current active zones:
# firewall-cmd –get-active-zones
Check the config of a zone
# firewall-cmd –info-zone=public
Open a port for a service in an active zone. Note that this is temporary. A reload or reboot of the firewall will blow this config away.
# firewall-cmd –zone=public –add-service=http
Close a port for a service in an active zone. Note that this too is temporary.
# firewall-cmd –zone=public –remove-service=http
To make this change active and permanent the command needs to be run twice, once with –permanent in place.
# firewall-cmd –permanent –zone=public –add-service=http
# firewall-cmd –zone=public –add-service=http
Now view the info for the zone and notice how the http service has been added.
Configuring a host to work as a NAT gateway
To enable NAT you first need to configure the kernel to forward IPv4 traffic. This can be done by adding the following file to
/etc/sysctl.d/98-ipv4-forward.conf with the following contents.
# cat /etc/sysctl.d/98-ipv4-forward.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
To immediately enable this setting then run the following command.
# sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
Next add your interfaces to different zones and reload the firewalld config.
# firewall-cmd –zone=external –add-interface=enp0s3 –permanent
# firewall-cmd –zone=internal –add-interface=Team1 –permanent
# firewall-cmd –complete-reload
Next enable masquarading on your external interface.
# firewall-cmd –zone=external –add-masquerade –permanent
Then add a postrouting rule using rich iptables rules.
# firewall-cmd –permanent –direct –passthrough ipv4 -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o enp0s3 -j MASQUERADE -s 10.0.0.0/24
There use to be an issue where after a restart the adapter would lose its zone config because it was not added into the ifcfg- file. This seems to no longer be the case in RHEL7.3, but it is something to watch for on the RHCE exam if it is an older version.
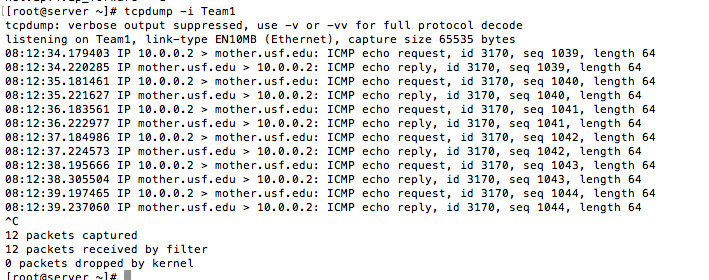
As a test I pinged an ip address on the internet from the client VM and ran tcpdump on the server VM. As you can see the ICMP traffic is traversing through the server VM as expected.
For more information on the configuring RHEL7 as a NAT Gateway check out this blog.
RHCE 7 Exam Objective: Configure IPv6
by jfargen on Nov.06, 2016, under Cert, RHCE, Training
Configure IPv6
This was a little painful, it maybe an issue with VBox, teaming, or IPv6. I expect in the EX300 exam simply adding the IPV6ADDR=wxyz.wxyz… and nmcli con reload will work with out any issues. To get this working on my VBox setup took a lot more work and research.
First, here is the configuration of the NAT network.
Next, there was an issue with duplicate local IPv6 addresses. First, I disabled IPv6 on the enp0s8 and enp0s9, then I disabled dad, on both the server and client VMs.
Here are the relevent sections in /etc/sysconfig/network-scrtips/ifcfg-enp0s[8-9]
IPV6INIT=no
IPV6_AUTOCONF=no
IPV6_DEFROUTE=no
IPV6_PEERDNS=no
IPV6_PEERROUTES=no
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
Then I added this file and contents to disable dad:
# cat /etc/sysctl.d/90-ipv6-disable-dad.conf
net.ipv6.conf.default.optimistic_dad=1
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_dad=0
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s8.optimistic_dad=1
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s8.accept_dad=0
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s9.optimistic_dad=1
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s9.accept_dad=0
net.ipv6.conf.Team1.optimistic_dad=1
net.ipv6.conf.Team1.accept_dad=0
net.ipv6.conf.all.use_tempaddr=-1
Then I went to this site to generate a local Unique Local Address (ULA):
You can just pick the first subnet.
My subnet was fdf8:d910:d680::/64.
I used fdf8:d910:d680::0001/64 server VM IPv6 address and fdf8:d910:d680::0002/64 for the client VM Ipv6 address.
Example: Add this line to /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-Team1 on the server VM
IPV6ADDR=fdf8:d910:d680::0001/64
Then start the VMs once this is completed.
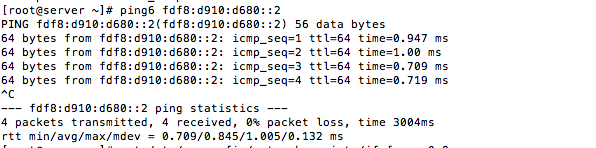
To test, I tried pinging the client VM from itself, which was successful.
Then I attempted to ping the client VM from the server VM which was also successful.
If you want my info on IPv6 their are excellent tutorials at the site TunnelBroker. They also have an interesting service that allows you to tunnel IPv6 over IPv4, but the last time I checked they had a feud with Cogent Communications that broke half the IPv6 internet.
RHCE 7 Begin Here
by jfargen on Nov.06, 2016, under Cert, RHCE, Training
The RHCE 7 is a comprehensive exam, Red Hat provides the exam objectives. I have copied the objectives to a seperate page, each objective will link to its own page covering that objective and the easiest/quickest/dirtiest way to address it.
But before you can begin you need to configure some virtual machines.
In my case I am running OS X + VirtualBox. In this case virtualbox gives me the flexibility I need to run multiple Linux VMs. Vbox has a snapshotting feature which will allow me to recover from a faulty configuration. In addition Vbox is a very mature product.
I have two RHEL7 (substitute CentOSY if you do not have access to RHEL7 with little worries) virtual machines, configured with 1 processor, 1GB RAM, 8GB storage, and 3 network adapters.
You might ask why there are three network adapters? This is not very unusual, you usually have a management interfaces, we will use the other two interfaces for a team (think bonded) interface, which is also the first exam objective.
Here is a screenshot of the first network adapter interface, as you can see it is a NAT interface, I also setup some port forwarding rules so I can run the VM headless and ssh directly from my terminal of choice in OS X.
Here is a screen shot of the second interface, the third interface should have the same network and config.
After the network is configured you can install the RHEL7 OS. After the OS is installed you should take a snapshot, then update the OS and take a snapshot, then you can begin the first exam objective. After you successfully complete an objective, take a snapshot, so you can recover from any issues you encounter.
RHCE 7 Exam Objective: Use network teaming
by jfargen on Nov.06, 2016, under Cert, RHCE, Training
Use network teaming or bonding to configure aggregated network links between two Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems
We will cover configuring a team interface in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 using the nmcli command line utility.
Protip: Don’t try to use the nmtui command, there are reports that there is a bug in this utility and that it will crash. Instead use the nmcli utility, I know it seems daunting but there are good example in the man pages. You can find the team example by viewing the nmcli manpage, at bottom you will find nmcli-examples.
Here is a sample of my theorhetical server config with a team interface configured with the ip of 10.0.0.1. It probably needs to be tweaked for a prod environment, like DEFROUTE=yes may not be a good idea, but it is quick and dirty and works.
First configure the team interface on both hosts, in this example I am using the enp0s8 and enp0s9 interfaces.
# nmcli con add type team con-name Team1 ifname Team1
# nmcli con add type ethernet con-name Team1-slave1 ifname enp0s8 master Team1
# nmcli con add type ethernet con-name Team1-slave2 ifname enp0s9 master Team1
Second, edit /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s[8-9] to ensure that the interfaces have ONBOOT=yes.
[root@server ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s8
TYPE=Ethernet
BOOTPROTO=dhcp
DEFROUTE=yes
PEERDNS=yes
PEERROUTES=yes
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6INIT=yes
IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes
IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes
IPV6_PEERDNS=yes
IPV6_PEERROUTES=yes
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
NAME=enp0s8
UUID=1ae65bbc-f27e-4e29-aec3-7ea30bc89171
DEVICE=enp0s8
ONBOOT=yes
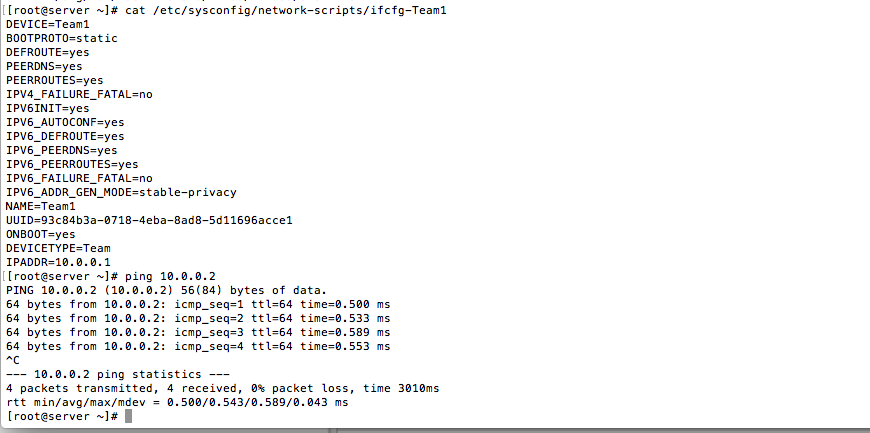
Next, edit /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-Team1, in this case I set BOOTPROTO=static, ONBOOT=yes, and IPADDR=10.0.0.1
[root@server ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-Team1
DEVICE=Team1
BOOTPROTO=static
DEFROUTE=yes
PEERDNS=yes
PEERROUTES=yes
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6INIT=yesIPV6_AUTOCONF=yes
IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes
IPV6_PEERDNS=yes
IPV6_PEERROUTES=yes
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy
NAME=Team1
UUID=93c84b3a-0718-4eba-8ad8-5d11696acce1
ONBOOT=yes
DEVICETYPE=Team
IPADDR=10.0.0.1
I just rebooted the server and client VMs in order to get the interfaces working, but you can try nmcli con reload.
Repeat with similar parameters for your client vm and test.
Here is some sample output showing the server host successfully pinging the client host.
RHCE 7 Exam Objectives
by jfargen on Nov.06, 2016, under Cert, RHCE, Training
RHCE 7 Exam Objectives
This page will contain the RHCE7 exam objectives for the exam EX300 published here on Sunday November 6, 2016. No warranty or guarantee that these topics will be applicable when you begin your review of the exam.
System configuration and management
- Use network teaming or bonding to configure aggregated network links between two Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems
- Configure IPv6 addresses and perform basic IPv6 troubleshooting
- Route IP traffic and create static routes
- Use firewalld and associated mechanisms such as rich rules, zones and custom rules, to implement packet filtering and configure network address translation (NAT)
- Configure a system to authenticate using Kerberos
- Configure a system as either an iSCSI target or initiator that persistently mounts an iSCSI target
- Produce and deliver reports on system utilization (processor, memory, disk, and network)
- Use shell scripting to automate system maintenance tasks
Network services
Network services are an important subset of the exam objectives. RHCE candidates should be capable of meeting the following objectives for each of the network services listed below:
- Install the packages needed to provide the service
- Configure SELinux to support the service
- Use SELinux port labeling to allow services to use non-standard ports
- Configure the service to start when the system is booted
- Configure the service for basic operation
- Configure host-based and user-based security for the service
HTTP/HTTPS
- Configure a virtual host
- Configure access restrictions on directories
- Deploy a basic CGI application
- Configure group-managed content
- Configure TLS security
DNS
- Configure a caching-only name server
- Troubleshoot DNS client issues
NFS
- Provide network shares to specific clients
- Provide network shares suitable for group collaboration
- Use Kerberos to control access to NFS network shares
SMB
- Provide network shares to specific clients
- Provide network shares suitable for group collaboration
SMTP
- Configure a system to forward all email to a central mail server
SSH
- Configure key-based authentication
- Configure additional options described in documentation
NTP
- Synchronize time using other NTP peers
Database services
- Install and configure MariaDB
- Backup and restore a database
- Create a simple database schema
- Perform simple SQL queries against a database