Tag: cert
RHCE 7 Exam Objective: Configure IPv6
by jfargen on Nov.06, 2016, under Cert, RHCE, Training
Configure IPv6
This was a little painful, it maybe an issue with VBox, teaming, or IPv6. I expect in the EX300 exam simply adding the IPV6ADDR=wxyz.wxyz… and nmcli con reload will work with out any issues. To get this working on my VBox setup took a lot more work and research.
First, here is the configuration of the NAT network.
Next, there was an issue with duplicate local IPv6 addresses. First, I disabled IPv6 on the enp0s8 and enp0s9, then I disabled dad, on both the server and client VMs.
Here are the relevent sections in /etc/sysconfig/network-scrtips/ifcfg-enp0s[8-9]
IPV6INIT=no
IPV6_AUTOCONF=no
IPV6_DEFROUTE=no
IPV6_PEERDNS=no
IPV6_PEERROUTES=no
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
Then I added this file and contents to disable dad:
# cat /etc/sysctl.d/90-ipv6-disable-dad.conf
net.ipv6.conf.default.optimistic_dad=1
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_dad=0
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s8.optimistic_dad=1
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s8.accept_dad=0
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s9.optimistic_dad=1
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s9.accept_dad=0
net.ipv6.conf.Team1.optimistic_dad=1
net.ipv6.conf.Team1.accept_dad=0
net.ipv6.conf.all.use_tempaddr=-1
Then I went to this site to generate a local Unique Local Address (ULA):
You can just pick the first subnet.
My subnet was fdf8:d910:d680::/64.
I used fdf8:d910:d680::0001/64 server VM IPv6 address and fdf8:d910:d680::0002/64 for the client VM Ipv6 address.
Example: Add this line to /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-Team1 on the server VM
IPV6ADDR=fdf8:d910:d680::0001/64
Then start the VMs once this is completed.
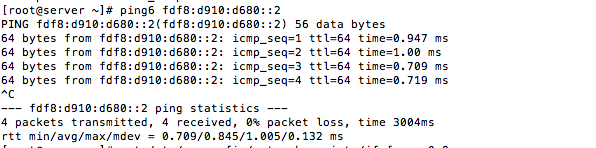
To test, I tried pinging the client VM from itself, which was successful.
Then I attempted to ping the client VM from the server VM which was also successful.
If you want my info on IPv6 their are excellent tutorials at the site TunnelBroker. They also have an interesting service that allows you to tunnel IPv6 over IPv4, but the last time I checked they had a feud with Cogent Communications that broke half the IPv6 internet.
RHCE 7 Exam Objectives
by jfargen on Nov.06, 2016, under Cert, RHCE, Training
RHCE 7 Exam Objectives
This page will contain the RHCE7 exam objectives for the exam EX300 published here on Sunday November 6, 2016. No warranty or guarantee that these topics will be applicable when you begin your review of the exam.
System configuration and management
- Use network teaming or bonding to configure aggregated network links between two Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems
- Configure IPv6 addresses and perform basic IPv6 troubleshooting
- Route IP traffic and create static routes
- Use firewalld and associated mechanisms such as rich rules, zones and custom rules, to implement packet filtering and configure network address translation (NAT)
- Configure a system to authenticate using Kerberos
- Configure a system as either an iSCSI target or initiator that persistently mounts an iSCSI target
- Produce and deliver reports on system utilization (processor, memory, disk, and network)
- Use shell scripting to automate system maintenance tasks
Network services
Network services are an important subset of the exam objectives. RHCE candidates should be capable of meeting the following objectives for each of the network services listed below:
- Install the packages needed to provide the service
- Configure SELinux to support the service
- Use SELinux port labeling to allow services to use non-standard ports
- Configure the service to start when the system is booted
- Configure the service for basic operation
- Configure host-based and user-based security for the service
HTTP/HTTPS
- Configure a virtual host
- Configure access restrictions on directories
- Deploy a basic CGI application
- Configure group-managed content
- Configure TLS security
DNS
- Configure a caching-only name server
- Troubleshoot DNS client issues
NFS
- Provide network shares to specific clients
- Provide network shares suitable for group collaboration
- Use Kerberos to control access to NFS network shares
SMB
- Provide network shares to specific clients
- Provide network shares suitable for group collaboration
SMTP
- Configure a system to forward all email to a central mail server
SSH
- Configure key-based authentication
- Configure additional options described in documentation
NTP
- Synchronize time using other NTP peers
Database services
- Install and configure MariaDB
- Backup and restore a database
- Create a simple database schema
- Perform simple SQL queries against a database